The massive (and often forced) shifting of workloads to a remote setting, the organization of disparate teams to maintain productivity from anywhere in the world, these are trying tasks for anyone employing high-throughput equipment and resource-intensive software. For a number of reasons, you cannot transfer them home, but you can still organize high-quality remote access from anywhere at no extra cost. We are going to tell you about the first way we have tested for maintaining convenient remote management from almost any device.
What’s up, doc?
The average employee just needs to connect to the remote desktop using the RDP protocol in order to access corporate resources from a laptop, and herein lies the problem for IT specialists: ensuring security. If a specialist needs resource-intensive applications that use 3D acceleration, this is a problem of a completely different kind.
Building Information Modeling (BIM), different types of design programs (CAD, CAM, etc.), geological modeling, numerous rendering tasks, working with neural networks and even application development - serious number crunching is impossible without GPUs, and to access a highly productive work station or server, the usual Remote Desktop is often not enough. It is usually impossible to install equipment at home: there are too many obstacles, such as the lack of the necessary infrastructure on site or an insufficiently high bandwidth in the local internet connections (the data for processing is usually stored within the corporate infrastructure).
At the same time, workstations with NVIDIA game cards are common in offices for such tasks, a situation which does not allow for using typical corporate solutions remotely.
Downsides of commercial solutions
The problem of keeping work from home at a productive level is usually solved with the help of special solutions (Citrix, Horizon) and hardware, such as cards and Teradici software.
-
These options might not be right for everyone because of:
-
The substantial cost of subscription / licenses;
-
The high complexity of software that cannot be installed by an untrained administrator;
-
The serious demands put upon the client device;
-
Other use limitations, i.e. the solutions do not work with game cards: their compatibility is with the NVIDIA Quadro line, which is even unavailable for all users at office workstations.
As we have already said, machines with NVIDIA gaming cards are more popular in offices. With this in mind, we have tested a more convenient and affordable option. Now, we will tell you about it.
The Free Alternative
The problems related to the remote use of the GPU are solved by Moonlight. . This free and open source software uses the NVIDIA GameStream protocol. It connects the server and client device and enables instant remote employee interaction with office desktops and workstations from anywhere.
-
It’s worth trying Moonlight for remote work if you work in:
-
BIM, CAD, CAM and other types of design applications
-
Design and training of neural networks, including data science
-
Pharmacological and medical research
-
Rendering
-
Software development.
-
Moonlight’s two main advantages:
-
Cross-platform Software. Client applications run on Windows, MacOS, Linux and Android;
-
Independence from vendor technologies - unlike NVIDIA Shield, Moonlight connects various devices. A compatible video adapter and the NVIDIA control panel software must be installed on the server, but the client may use a video card of any manufacturer on his device.
-
Other benefits of Moonlight:
-
Low latency connection and the ability to get up to 60 frames per second on the remote device
-
The ability to transfer images with a resolution of up to 4K
-
Ease of use
Installation Features of Moonlight
The installation process is described in detail in the developer’s repository on GitHub, and we will focus on its key and non-obvious points. Deploying the software takes several large steps on the client side (the user's local device) and on the server or workstation (the host).
First, let’s take an overview of Moonlight’s architecture:
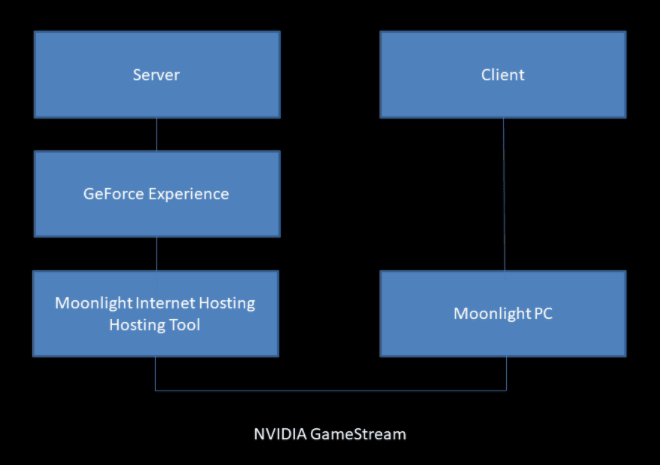
Now, let’s take a closer look at some important points
First, the host must have an NVIDIA graphics card which supports the NVIDIA control panel (starting from the GeForce GTX 650 and older), the Moonlight Internet Hosting Tool, and the NVIDIA Control Panel application. Only the Moonlight app is needed on the client device.
The second point: the panel should be configured to work with NVIDIA Shield. To do this, just go to the application settings and set the switch to the "on" (green) position and add the path to the mstsc.exe utility: "C: \ windows \ system32 \ mstsc.exe".
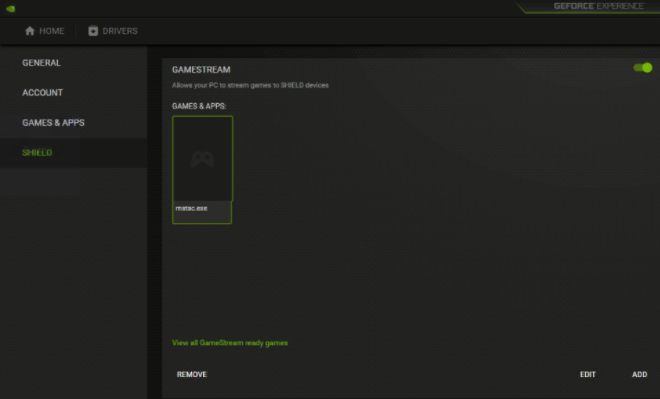
This setting provides remote desktop access through Moonlight. When connecting to the server for the first time, you must enter the password for the NVIDIA control panel (it will be displayed in the Moonlight client).

-
The password will be remembered for the server's IP address. Moonlight listens on the following ports:
-
TCP 47984, 47989, 48010;
-
UDP 47998, 47999, 48000, 48002, 48010.
-
Third point: you should not use the RDP protocol to remotely control the server as it does not allow you to configure NVIDIA Shield. To access the desktop, you need a VNC client:
-
UltraVNC
-
Anydesk
-
TeamViewer
The stability and comfort of working with Moonlight depends on the quality of the Internet connection. The developers recommend using the program when the outgoing stream speed from the user's client device to the server is at least 5 Mbps. The client usually needs a cable Internet connection to do this.
Thus, at the recommended speed, the tests show that a stable image can be maintained only at a resolution of 600x800. And on a modem with DOCSIS / DSL 6M, we managed to see a standard picture in 3D with a resolution of 1024x768. In practice, it turned out that for HD and 4K you need a fiber-optic Internet connection with a speed of at least 100 Mbps and a similar connection for the server/workstation.
Moonlight allows for the flexible management of the image quality from the host to the user's local device:
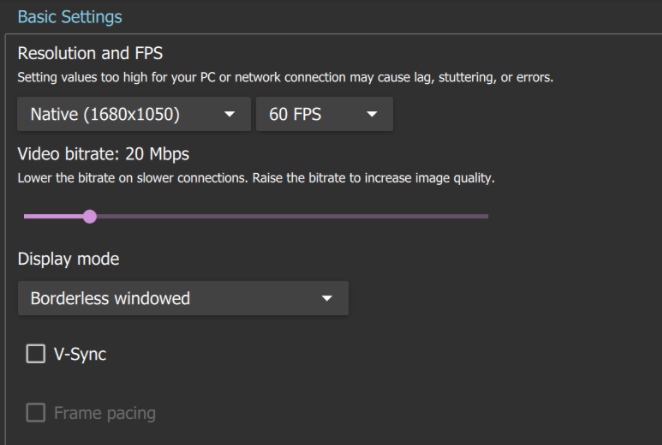
The fourth critical point: by default, the bit rate is set depending on the speed of the Internet connection. The better it is, the higher the image quality and the lower the latency. To select the required bitrate, you can use the following table:
| Resolution | Frames per second (FPS) | Bitrate (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|
| 720p, 1280 x 720 | 30 | 5–10 |
| 1080p, 1920 x 1080 | 60 | 20 |
| 1440p, 2560 x 1440 | 60 | 40 |
| 4K/2160p, 3840 x 2160 | 60 | 80 |
| Resolution 720p, 1280 x 720 | |
| Frames per second (FPS) | 30 |
| Bitrate (Mbps) | 5 - 10 |
| Resolution 1080p, 1920 x 1080 | |
| Frames per second (FPS) | 60 |
| Bitrate (Mbps) | 20 |
| Resolution 1440p, 2560 x 1440 | |
| Frames per second (FPS) | 60 |
| Bitrate (Mbps) | 40 |
| Resolution 4K/2160p, 3840 x 2160 | |
| Frames per second (FPS) | 60 |
| Bitrate (Mbps) | 80 |
And fifth: the quality of working with Moonlight is also affected by the latency of the Internet connection. It can be influenced by the actual distance between the server and the client, the network topology, channel load, equipment failures, and other reasons. In the course of our testing, the latency did not exceed 80 ms, which corresponds to the indicator required for comfortable gaming and working with resource-intensive software.
For Moonlight to work correctly on the server, a monitor must be connected to the GPU or an HDMI / Display Port dummy must be inserted, otherwise the resolution will not rise above the base 800x600.
For more information, read our detailed user instruction manual for Moonlight on HOSTKEY servers.
Tried and Tested: examples of working with Moonlight
-
To illustrate just how the software works, we have conducted a few tests:
-
watch Big Buck Bunny at 60fps in 4K;
-
The Junk Shop scenes in Blender;
-
Hellblade Senua's Sacrifice game play at the maximum graphics settings.
We decided to conduct a work scenario test at our HOSTKEY office using the following build:
-
Operating System: Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Standard
-
CPU: Intel Xeon E-3-1230, v6, 3,5 GHz
-
GPU: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti (11 GB)
-
RAM: 16 GB
When launching Moonlight on the client side, we got a stable performance with a resolution of 3840x2160 and 60 FPS and a bitrate of 80 Mbps. The application response was smooth and almost indistinguishable from controlling it directly on the host device.
-
Here you can watch the recordings of our streams:
-
Big Buck Bunny video
-
Blender
-
Hellblade Senua's Sacrifice
So, the problem of working remotely with resource-intensive applications has been solved, and Moonlight is far from the only way to ensure a comfortable workflow out of the office.
In the following posts, we will talk about other options for full remote access to software and equipment for rendering, designing and training neural networks.


