TrueNAS SCALE¶
In this article
Information
TrueNAS - a FreeBSD-based distribution for network storage organization. TrueNAS allows solving many tasks related to data storage and processing It provides centralized data storage, and enables access to data from different locations and devices. TrueNAS supports various protocols and interfaces, including SMB, NFS, AFP, FTP, iSCSI, and others, which allows it to be used for various tasks.
Attention
While accessing the web control panel, you may see a warning message Your connection is not private. To proceed, click on the text Proceed to "TRUENAS_IP" (unsafe). You can follow our instructions to prevent the appearance of this message.
Note
Unless otherwise specified, by default we install the latest release version of software from the developer's website or operating system repositories.
Authorization¶

After clicking the link, you need to enter the username and password that are provided in an email sent to your email address when the server is ready for operation after software deployment.
The left side of the screen contains the navigation menu, which includes the following sections:
- Dashboard - Provides general information about the system;
- Storage - Manages Storage;
- Dataset - Manages Datasets;
- Shares - Manages File Sharing;
- Data Protection - Manages Data Protection tasks;
- Network - Manages Network Interfaces;
- Credentials - Configures and Manages user credentials and access rights;
- Virtualization - Manages VMs;
- Apps - Manages applications;
- Reporting - Monitors resource usage;
- System Settings - system configuration.
Dashboard¶
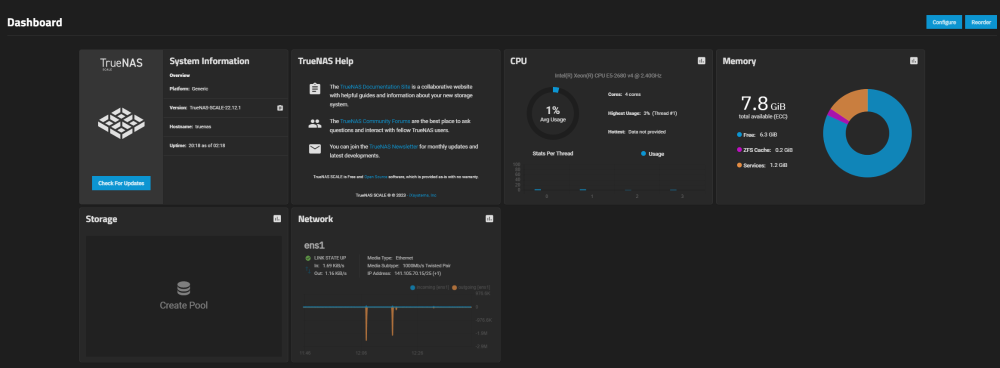
After successful authorization, you will see a dashboard with general system information:
- System Information - provides general system information;
- TrueNAS Help - provides links to documentation, technical support, and community forums;
- CPU - displays information about the processor;
- Memory - provides information about memory usage;
- Storage - displays information about storage;
- Network - provides information about network connections.
Storage¶
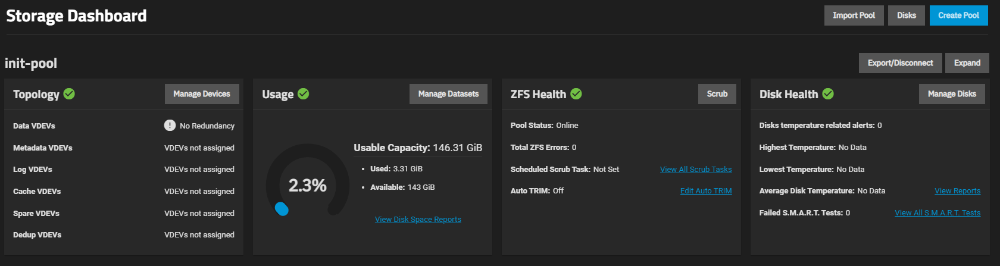
The Storage section in the TrueNAS SCALE management interface is used to manage data storage on the server. In this section, you can create, configure, and manage storage pools.
The creation of a pool¶
A pool is a logical storage container that combines multiple physical disks into a single storage space. It provides high reliability and performance for data storage and simplifies storage management.
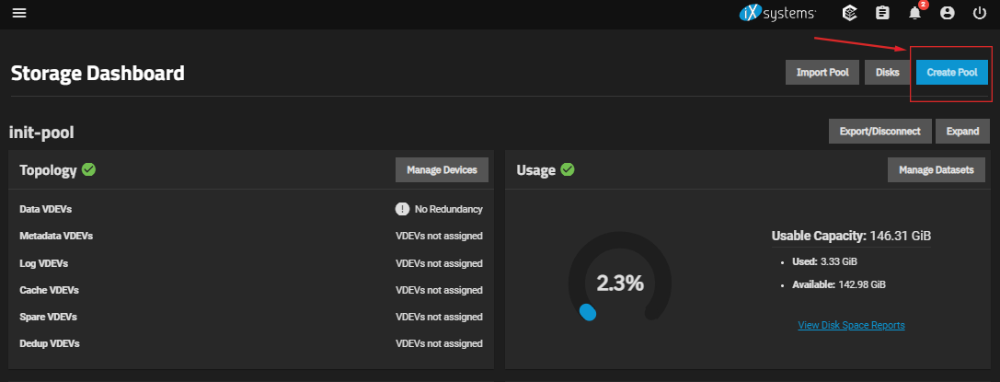
In TrueNAS SCALE, a pool allows you to create datasets that can be used for storing different types of data, such as Windows Shares, Unix Shares, Block Shares, WebDAV Shares, and others. Pools can also be used to create virtual machines and containers. To create a new pool, go to the Storage section and click on the Create Pool button.:
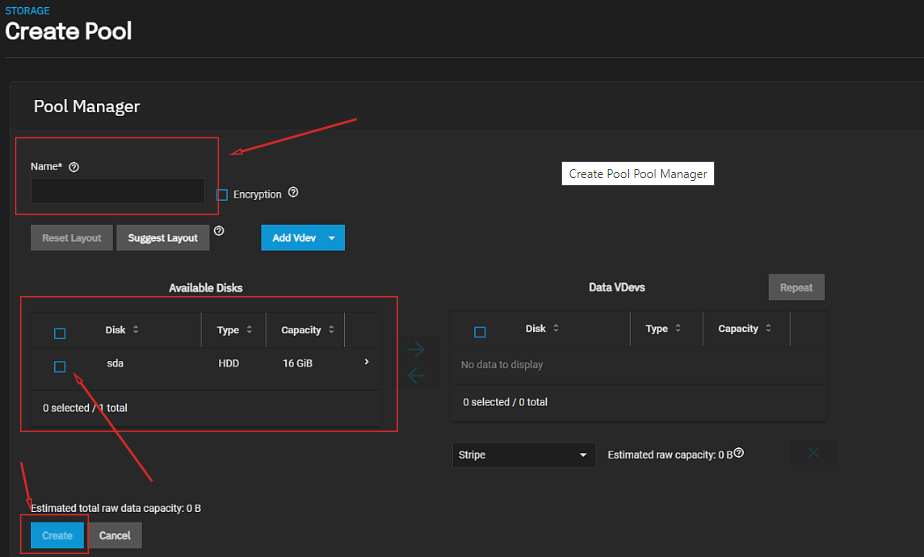
Specify the name of the new pool, the disk, and configure additional settings if necessary (refer to the Developer Documentation), then click the Create button:
Dataset¶
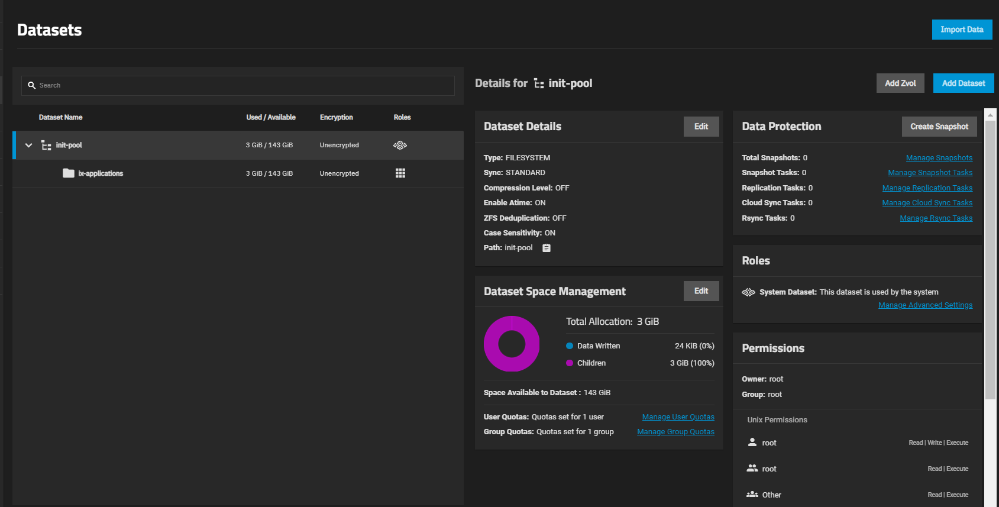
The Dataset section in the TrueNAS SCALE management interface provides functionality for managing datasets on file servers. Datasets can be configured to store various types of files and serve different data access protocols.
In this section, you can create new datasets, edit and delete existing ones, as well as manage access rights to them. Additionally, you can configure data backup and restoration functions, as well as manage snapshots, which allow you to preserve the state of data at a specific moment in time for fast recovery in case of system failures.
Furthermore, in the Datasets section, you can configure data compression features, which help save disk space and increase data access speed. Overall, the Datasets section offers a wide range of capabilities for managing datasets in the TrueNAS SCALE system.
Shares¶
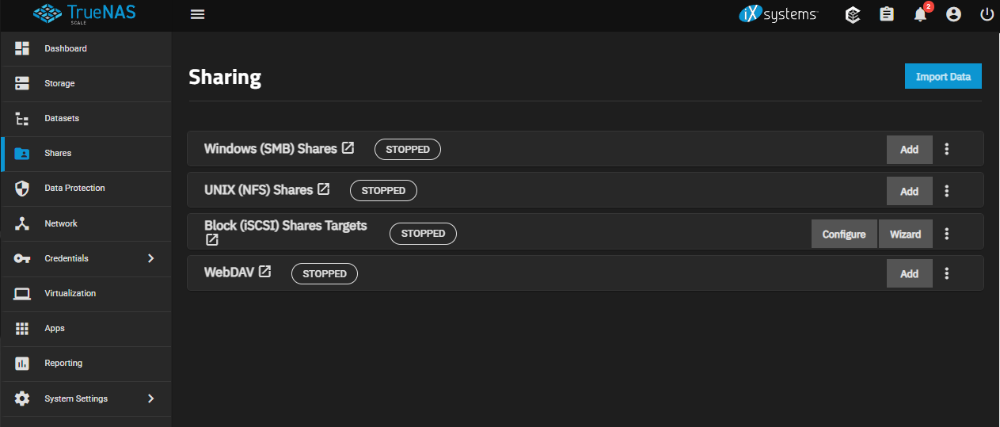
File sharing is one of the main advantages of a NAS. TrueNAS facilitates collaboration through shared network resources. TrueNAS SCALE allows you to create and configure target block (iSCSI) shares, Windows SMB shares, Unix (NFS) shares, and WebDAV shares.
There are four types of file sharing available:
- Windows Shares (SMB) - a protocol for file sharing between computers in a network, commonly used in the Windows operating system. In TrueNAS, this protocol is used to create network shares and provide shared access to files between computers in a local network.
- Unix Shares (NFS) - a protocol for file sharing between computers in a network, commonly used in Unix-like operating systems. In TrueNAS, this protocol is used to create network shares and provide shared access to files between computers in a local network.
- Block Shares (iSCSI) - a protocol that allows for the creation of virtual disks on the server and sharing them with computers in a network. It enables them to be used as regular physical disks on remote computers. This allows for shared resources and collaboration on documents and files between different operating systems. Block Shares in TrueNAS also provides data access security by allowing the configuration of authorization and authentication levels for users, as well as setting different access rights for virtual disks. Additionally, TrueNAS supports data encryption features for secure data transmission over the network, enhancing the security of transferring confidential information.
- WebDAV Shares - allows for the creation of shared folders and files on the server, which can be accessed by computers in the network for read and write operations. The WebDAV protocol also supports file locking, versioning, access control management, and other useful features for file and data management.
Data Protection¶
The Data Protection section allows you to configure multiple duplicate tasks to protect and backup data in case of disk failures.
Network¶
The Network section is used for configuring and managing network interfaces and network settings. In this section, you can configure interface parameters such as speed and duplex settings, VLAN, LAGG groups (Link Aggregation Groups), routing, DNS servers, and more. You can also configure network-level protocol parameters such as IPv4, IPv6, and DHCP settings, as well as access parameters for network resources such as SMB, NFS, and iSCSI. Additionally, in the Network section, you can configure network security and protection parameters, such as firewall and VPN server settings.
Credentials¶
The Credentials section is used for configuring and managing user credentials and access rights. In this section, you can configure authentication parameters, such as authentication methods, set up LDAP servers, configure SSL/TLS certificates, create and manage users and groups, assign access rights to network resources such as SMB, NFS, and iSCSI. Additionally, in the Credentials section, you can configure security and protection settings, such as two-factor authentication and password protection settings.
Virtualization¶
In the Virtualization section, you can configure virtualization parameters, create and manage virtual machines, configure their settings, install operating systems and applications, configure network settings, create virtual machine images, and more. Additionally, in the Virtualization section, you can configure virtual machine security and protection settings, such as firewall settings and password protection settings. TrueNAS SCALE allows users to configure six different virtual machine segments while creating a virtual machine.
Several virtualization options are presented in this section:
- Adding and Managing VMs - allows you to create isolated environments for running and testing applications and operating systems. VMs allow you to use server resources more efficiently by allowing you to run multiple virtual machines on a single server.
- Adding and Managing VM Devices - creating various types of virtual devices, such as virtual disks, network interfaces, sound cards, video cards, USB devices, etc.
- Accessing NAS From a VM - allows you to exchange data between a virtual machine and a file server.
Apps¶
In the Apps section, you can install and manage various applications and services (Minio, Nextcloud, Plex, Syncthing, WG Easy, etc.) directly from the TrueNAS management interface.
Information
A full list of available applications can be found here.
Add an Application¶
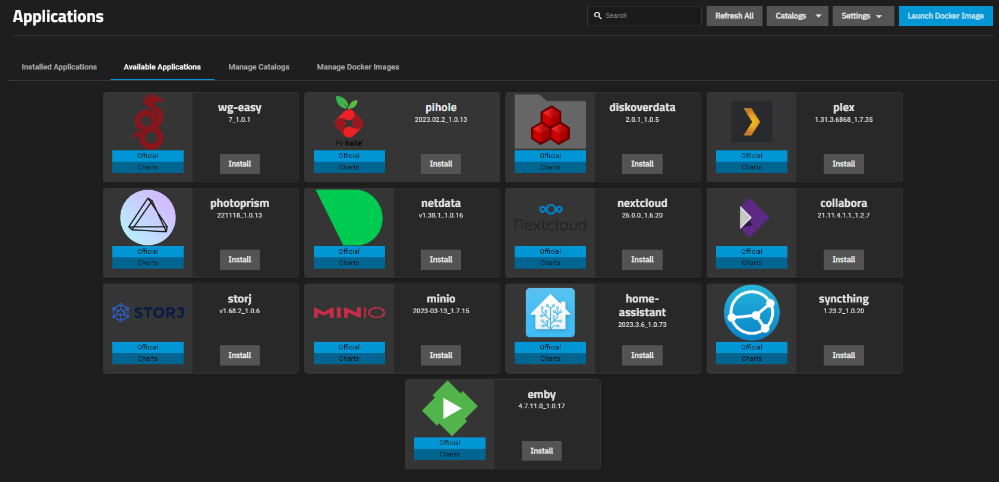
To install a new application, go to the APPS section, select Available Applications and click on the Install button in the application card.
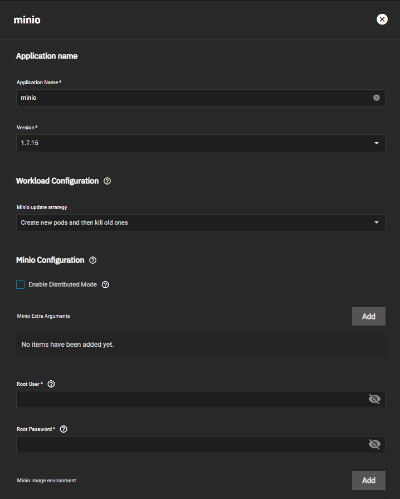
Fill in the necessary details in the opened menu (the data may vary depending on the installed application):
Installed applications can be managed and edited in the Installed Applications section:
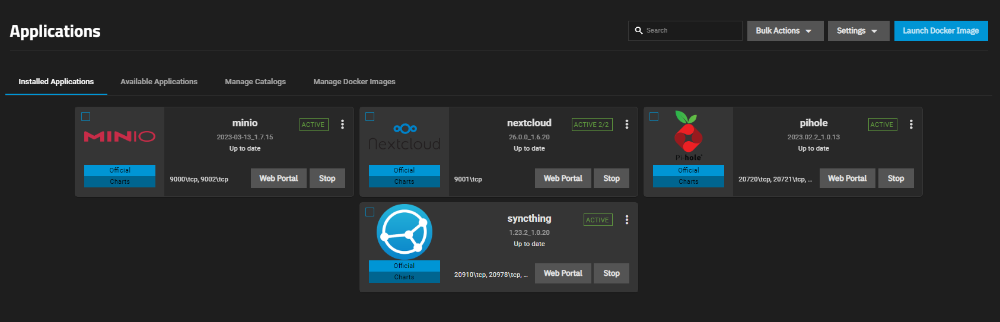
To access the management menu of the installed application, click on the Web Portal button. The application will open in a separate tab. You should use the credentials provided during the installation of the application for authentication.
Example of MinIO interface:
Remove an Application¶
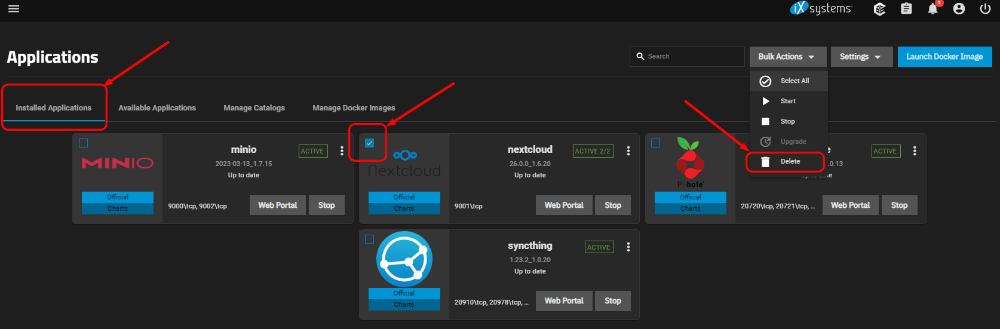
To remove an installed application, go to the Installed Applications section. Check the box next to the application, click on the dropdown menu Bulk Actions and select Delete.
Attention
Some applications may be incompatible with others installed on the server. Before installing an application, please review its documentation to ensure compatibility with other applications and services.
Attention
Some applications may require additional settings, such as ports, protocols, etc. Before installation, review the documentation to ensure proper configuration.
Attention
Some applications may have restrictions on commercial use or usage in certain countries. Please review the licensing terms before installation to ensure compliance with your country's regulations.
Reporting¶
Access various reports on the server's status and its components. In this section, you can find information about CPU load, memory usage, disk space, network traffic, and other server’s parameters.
System Settings¶
Access various system and server settings. In this section, you can configure network, security, data storage, management system, and other parameters. Some of the functions available in the System Settings section include:
- General: Configure general server parameters such as hostname, time zone, language, etc.
- Advanced: Configure more advanced system parameters such as network settings, security settings, power-saving settings, memory settings, etc.
- Boot: Configure server boot parameters such as boot order, kernel parameters, etc.
- Services: Configure various services and applications running on the server, such as FTP server, SSH server, SMB server, etc.
- Shell: Access the server's command shell and perform manual operations